Despite an unfavorable regulatory environment stopping traditional acquisitions, tech giants are actively investing billions of dollars in emerging technologies.
Amazon recently made its largest venture deal, a $2.75 billion investment in the artificial intelligence startup Anthropic.
This move reflects the ongoing AI gold rush, where major tech companies are aggressively expanding their portfolios to stay competitive in a market projected to exceed $1 trillion in revenue within the next decade.
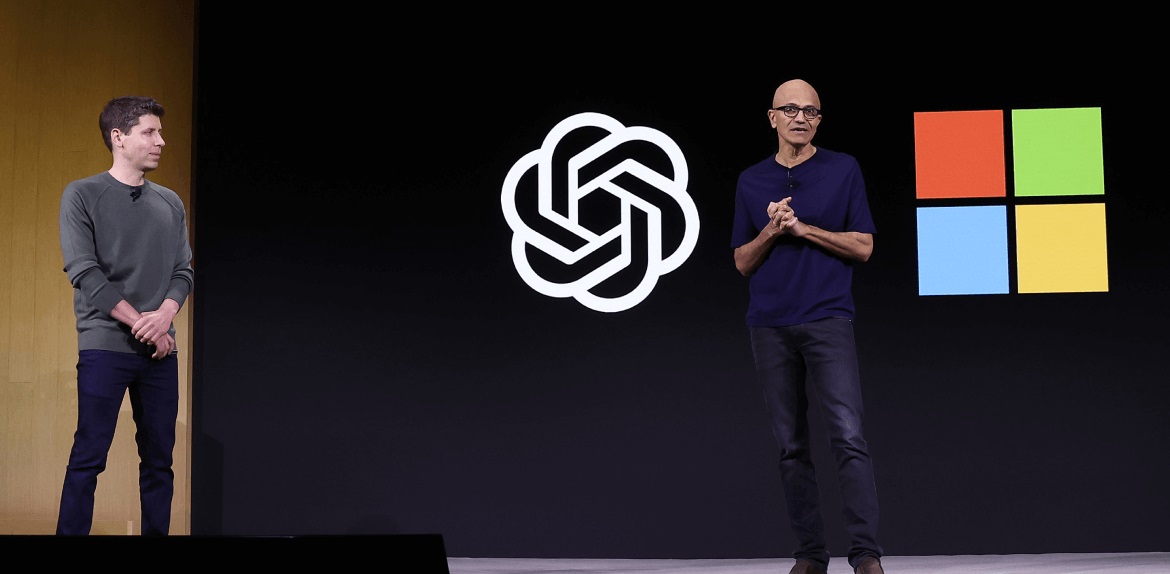
Anthropic’s AI model, Claude, directly competes with offerings from industry heavyweights like Microsoft’s OpenAI and Google’s Gemini.

As companies rush to integrate generative AI into their products and services, investments in this field have skyrocketed.
In 2023 alone, investors poured a combined $29.1 billion into nearly 700 generative AI deals, marking a substantial increase from the previous year.
The hefty sums are essential due to the considerable costs associated with building and training AI models, particularly the need for specialized chips primarily supplied by Nvidia.
Tech giants like Nvidia not only develop chips but also invest in emerging AI companies to ensure widespread deployment of their technology.
Strategic alliances with cloud providers, such as Microsoft, Google, and Amazon, offer startups access to resources and infrastructure, facilitating customer acquisition.

In the Amazon-Anthropic deal, the collaboration extends beyond investment, with Anthropic leveraging Amazon Web Services (AWS) for computing needs and utilizing Amazon’s chips.
Similar partnerships exist between other tech companies and AI startups, with mutual benefits for both parties.
While some tech giants focus on internal AI development, others invest in external startups to access fundamental intellectual property.
However, increased regulatory scrutiny poses challenges, prompting companies to explore alternative investment structures that comply with regulatory requirements.
Investments like Microsoft’s profit-sharing agreement with OpenAI and Amazon’s deal with Anthropic demonstrate this shift towards innovative partnerships rather than conventional acquisitions.
Regulators, including the Federal Trade Commission (FTC), are closely monitoring AI investments and partnerships among tech giants.
This scrutiny highlights the importance of having access to fundamental intellectual property in the rapidly evolving AI ecosystem.





Leave a Reply