NGate is a new Android malware that targets NFC technology to steal financial information from payment cards. By capturing data from the NFC chip on victims’ cards and relaying it to the attacker’s device, NGate enables unauthorized transactions and cash withdrawals.
This malware has been active since November 2023 and is associated with a broader trend of cyberattacks involving PWAs and WebAPKs, as highlighted in a recent ESET report focusing on activities in Czechia.
The attack begins with phishing methods such as malicious texts, automated calls, or harmful advertisements designed to lure users into installing a rogue PWA or WebAPK. These deceptive apps are often presented as essential security updates and use official banking logos and interfaces to trick users into entering their banking credentials.
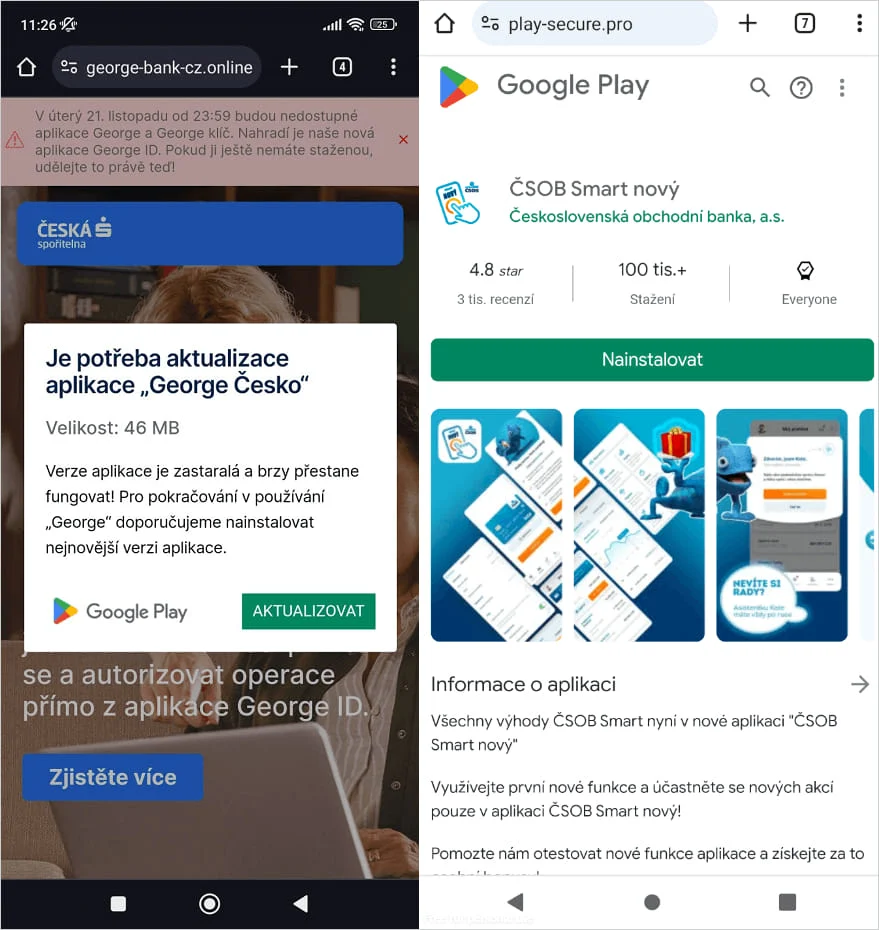
After the initial phishing step, NGate is installed through a subsequent phase. The malware incorporates an open-source tool named ‘NFCGate,’ initially created for NFC testing. This tool allows NGate to capture and relay NFC data from nearby payment cards to an attacker’s device, which can then be used to make unauthorized payments or withdraw cash from ATMs.
Additionally, NGate has capabilities beyond financial theft. It can clone NFC access cards and tokens, potentially leading to unauthorized access to secure areas or transport systems. The malware can also capture card PINs through social engineering tactics, where attackers impersonate bank employees to trick victims into providing sensitive information.
To mitigate risks associated with NGate, users should disable NFC on their devices when it is not in use. They should also be cautious with app permissions, only install apps from reputable sources, and avoid installing PWAs and WebAPKs unless absolutely necessary. This proactive approach can help protect against such sophisticated malware threats.







Leave a Reply