Android Lollipop, released in November 2014, marked a significant update to the Android operating system. Revealed at Google I/O earlier that year, it introduced a sleek Material Design aesthetic and a range of new features under its version numbers, Android 5.0 and 5.1.1. The Nexus 6, manufactured by Motorola, was the first device to ship with Lollipop pre-installed, showcasing its capabilities to the world.
Fast forward to today, and Google has made headlines by officially ending support for Android Lollipop. With less than 1% of active Android devices still running this older version, Google has decided to halt updates to Google Play services for these devices.
This move is aimed at enabling Google to concentrate its resources on more recent versions of Android, enhancing features and bolstering security for a larger portion of its user base.
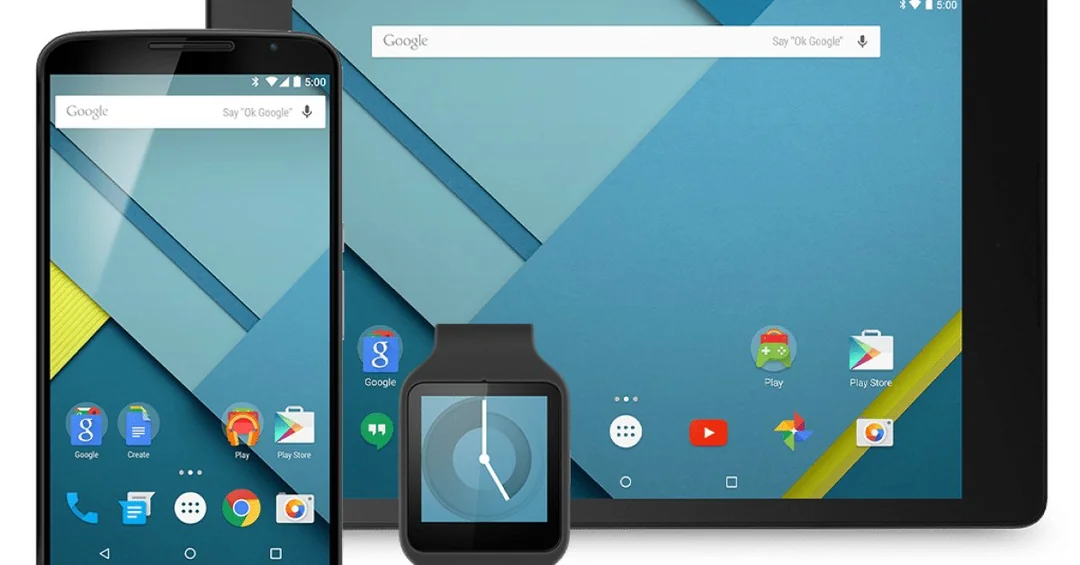
For users still holding onto Lollipop devices, this decision means they won’t receive future updates, including crucial security patches and compatibility fixes for Google apps reliant on updated services. While their devices will continue to function, they may find limitations in accessing newer app features and services that require more modern Android versions.
Google’s strategy reflects a broader industry trend of encouraging users to upgrade to newer Android releases for improved functionality and security. Android Marshmallow (6.0) and newer versions remain supported, ensuring users have access to the latest advancements and protections in the Android ecosystem.
Looking ahead, Google continues to evolve its Android platform, with Android 14 as the latest stable release and Android 15 currently in beta. Moving away from dessert-themed names, these updates underscore Google’s ongoing commitment to innovation and user experience across its diverse range of Android devices.
As technology advances, Google aims to keep Android users equipped with the best features and protections available in the mobile landscape.






Leave a Reply